active site of an enzyme
Role of Active Site. The enzyme-substrate complex is a 3 D structure.
 |
| What Is The Active Site Of An Enzyme What Are Enzymes How Do They Work How Do An Enzyme And A Substrate Bind |
The active site is a small region of the enzyme that binds to the substrate and it is where the chemical reaction takes place.

. In the lock and key hypothesis the shape of the active site matches the shape of its substrate molecules. Binds allosteric regulators of the enzyme. The initial binding of substrate and enzyme occur through the non-covalent bond. In the active site amino acids of the enzyme protein will.
Definition of Enzymes Active Site Key Points. Active sites are important because they are responsible for the catalytic activity of an enzyme. What is active site of enzyme in biology. A higher temperature generally makes for higher rates of reaction enzyme-catalyzed or otherwise.
There are two. It is generally found on the surface of enzyme and in some enzyme it is a Pit like structure The active site is a three-dimensional cleft formed by groups that come from different parts of the amino acid sequence. Some enzymes have to be activated in order to work. These pockets contain the active site which is the area of an enzyme where the substrate binds and the chemical reaction takes place.
The AA can be the same or different from the ones used in substrate binding. While in some a single reactant is broken down into different products. The active site consists of residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate binding site and residues that catalyse a reaction of that substrate catalyt. Only this region of the enzyme binds to the substrate.
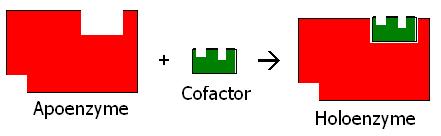
Binds allosteric regulators of the enzyme is inhibited by the presence of a coenzyme or a cofactor C. The enzyme including its active site will change shape and the substrate no longer fit. Methods in Enzymology 2016 Download as PDF About this page Repair of Double-Strand Breaks by Nonhomologous End Joining P. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate and residues that catalyse a reaction of that substrate.
The active site of an enzyme which frequently exists in what is called close association with the enzyme is the location at which all catalytic chemical reactions of that enzyme occur an exception is in certain dehalogenase enzymes in which the active site is actually inside the substrate. Active sites of the enzyme is that point where substrate molecule bind for the chemical reaction. Site-directed mutagenesis to disrupt catalysis but not substrate binding. 1 of 16 Active site of an enzyme May.
Solution Verified by Toppr The active site is the region of the enzyme where substrate molecule bind and undergo a chemical reaction. Enzyme active sites achieve TS stabilization by forming critical interactions with substrate s. Enzymes have active sites to bind to the substrate enzyme-substrate complex forming products by allowing the formation of bonds between the substrates. The active site of an enzyme is the region that binds substrate molecules.
The active site of an enzyme is the region that A. Notarangelo in Stiehms Immune Deficiencies Second Edition 2020 Definition. Lysozyme interacts with its polysaccharide substrate by binding a chain of six sugars in a groove along the enzyme surface cleaving at the center of the chain. Binds not competitive inhibitors of the enzyme D.
The active site of the enzyme is formed by the folding pattern of the protein. What happens when the active site of an enzyme is altered by changing pH or temperature. They help the substrate fit into the active site. Activators are effectors that bind to an allosteric site and help the substrate to bind.
Moskwa in Genome Stability 2016 2112 DNA-PKcs DNA-Dependent Protein Kinase Catalytic Subunit. The active site is a groove or pocket formed by the folding pattern of the protein. Active Site Binding Theories. This is crucial for the enzymes.
The active site possesses amino acid residues that participate in the catalytic reaction of the enzyme. Active site amino acid residues often have acidic or basic. Binds substrates for the enzyme. How many amino acids are in the active site.
The place where these molecules fit is called the active site. 19 it is the most. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze reactions in cells. Higher temperatures disrupt the shape of the active site which will reduce its activity or prevent it from working.
Methods in Enzymology 2016 View all Topics Download as PDF About this page Severe combined immune deficiency Fabio Candotti. Cofactors may also be required to turn on an enzyme. These active sites have large numbers of acid and base side chains. The catalytic active sites of enzymes be defined using modern computational program working with a data base of enzyme structure.
The active site is formed by the contribution of amino acid residues specific positions. Enzymes are globular proteins with a three-dimensional structure. In biology and biochemistry the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The site of an enzyme where a catalytic reaction occurs when the enzyme and substrate specifically bind to each other.
Only this region of the enzyme binds to the substrate. The active site is a groove or pocket formed by the folding pattern of the protein. Because enzymes like all proteins are made of amino acids there. The active site of an enzyme is the region that A.
Namrata Chhabra Follow Advertisement Recommended Mechanism of enzyme action Namrata Chhabra Active site of enzyme avinash tiwari. The enzyme - substrate complex is a 3 D structure. Lysozyme is an enzyme found in tears nasal secretions and the white of avian eggs which hydrolyzes the polysaccharides found in many bacterial cell walls. Answer 1 of 3.
Features that Determine Active Site Specificity. PH can also affect enzyme function. Products leave the active site of the enzyme and again that enzyme is ready to bind another substrate. Active Site Definition.
Amino acid mutation in the active site does not affect catalytic activity but substrate binding. An active site is a specific location found in the enzyme where a substrate binds to catalyze the reaction. 14 2020 5 likes 1180 views Education The active site takes the form of a cleft or pocket which is formed by groups that come from different parts of the amino acid sequences. The active site is the region of the enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo chemical reaction.
A region on an enzyme molecule that catalyzes a reaction is known as the active center of the enzyme. In biology the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The enzyme changes shape on substrate binding. The volume of the catalytic active sites is well defined by modern computational analysis of protein structure.
S583 phosphorylation stabilizes enzyme active site Residue S583 is located in the VEFS domain of SUZ12 which associates with the SET domain of EZH2 and is essential for the enzymatic activity 8 9. Factors that may affect the active site and enzyme function include. Enzyme Active Site Enzyme active sites achieve TS stabilization by forming critical interactions with substrate s. The enzyme will have been denatured.
Although the active site occupies only 1020 of the volume of an enzyme. The active site of an enzyme is the region that binds the substrates and cofactor if any The interaction of the enzyme and substrate at the active site promotes the formation of the transition state.
 |
| Question Video Defining The Key Terms Enzymes Substrates And Active Sites Nagwa |
 |
| Solved I Label The Image Below With The Following Terms Chegg Com |
 |
| Active Site Of An Enzyme Definition Mechanism Characteristics Role Biology Reader |
 |
| Active Site The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary |
 |
| Protein The Role Of The Active Site Britannica |
Posting Komentar untuk "active site of an enzyme"